Koxkar [Candidate]
Integrated CryoNet Cluster Information
Stations in This Site
This site is comprised of the following stations:
- Terminus Station - Contributing Station
- Lower Station - Contributing Station
- Middle Station - Contributing Station
Broad Research Focus
The Koxkar site focus on various aspects of large valley mountain glaciers including, for example, glacier physics, historical and current glacier changes, meltwater runoff characteristics, projections of glacial features in a changing climate.
Representativeness of the Cluster
The Koxkar site is located in western Tien Shan where many large valley glacier are nourshed. These glaciers contribute large proportion of fresh water to the extreme arid lowland - the Tarim Basin, and thus, is very important to maintain the functionality of the populated society. The basecamp of the site is located near the terminus of one of the large glaciers - the Koxkar Glacier where glacial features are similar to other big ice mass in the vicinity. Long-term observations upon glacier and glacial runoff in the Koxkar site will obtain unique and precious dataset of large valley glaciers with complex landscape to study glacier responses in a changing climate.
Cluster Facilities
A temporary dwelling with area of 230 square meters was built in the site to accomodate the faculty staffs and researchers Indoor toilet and shower room are available. Internet web and cellphone services are provided.
Data Information
- Are the data quality controlled? yes
- How are the data accessible?
- Data availability (may depend on the variable measured):
Publications
Han Haidong. 2013. AIWA 1.0: A universal graphical user interface for distributed hydrological modeling. Computers & Geosciences, 59: 108-115.
Han Haidong, Liu Shiyin, Wang Jian, Wang Qiang, Xie Changwei. 2010. Glacial runoff characteristics of the Koxkar glacier, Tuomuer-Khan Tengri Mountain Ranges, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 61(4)?665-674.
Han Haidong, Wang Jian, Wei Junfeng, Liu Shiyin. 2010. Backwasting rate on debris-covered Koxkar Glacier, Mt. Tuomuer, China. Journal of Glaciology, 56(196)?287-296.
Han Haidong, Ding Yongjian, Liu Shiyin.2006. A simple model to estimate ice ablation under a thick debris layer. Journal of Glaciology, 52(179)?528-536.
Additional Information Documents
Measurements
The measurements made at Koxkar are listed in the following tables. This is a combination of measurements made at the stations within the site, where the start and end years in the tables are the earliest and latest years of measurement. (Note: If End Year is blank, measurements are ongoing.)
Cryosphere Measurements
| Atmosphere Measurements
|
Measurement Notes and Other Measurements
| Category | Description or List |
|---|---|
| Hydrology | Meltwater runoff, since 2003, continuous. |
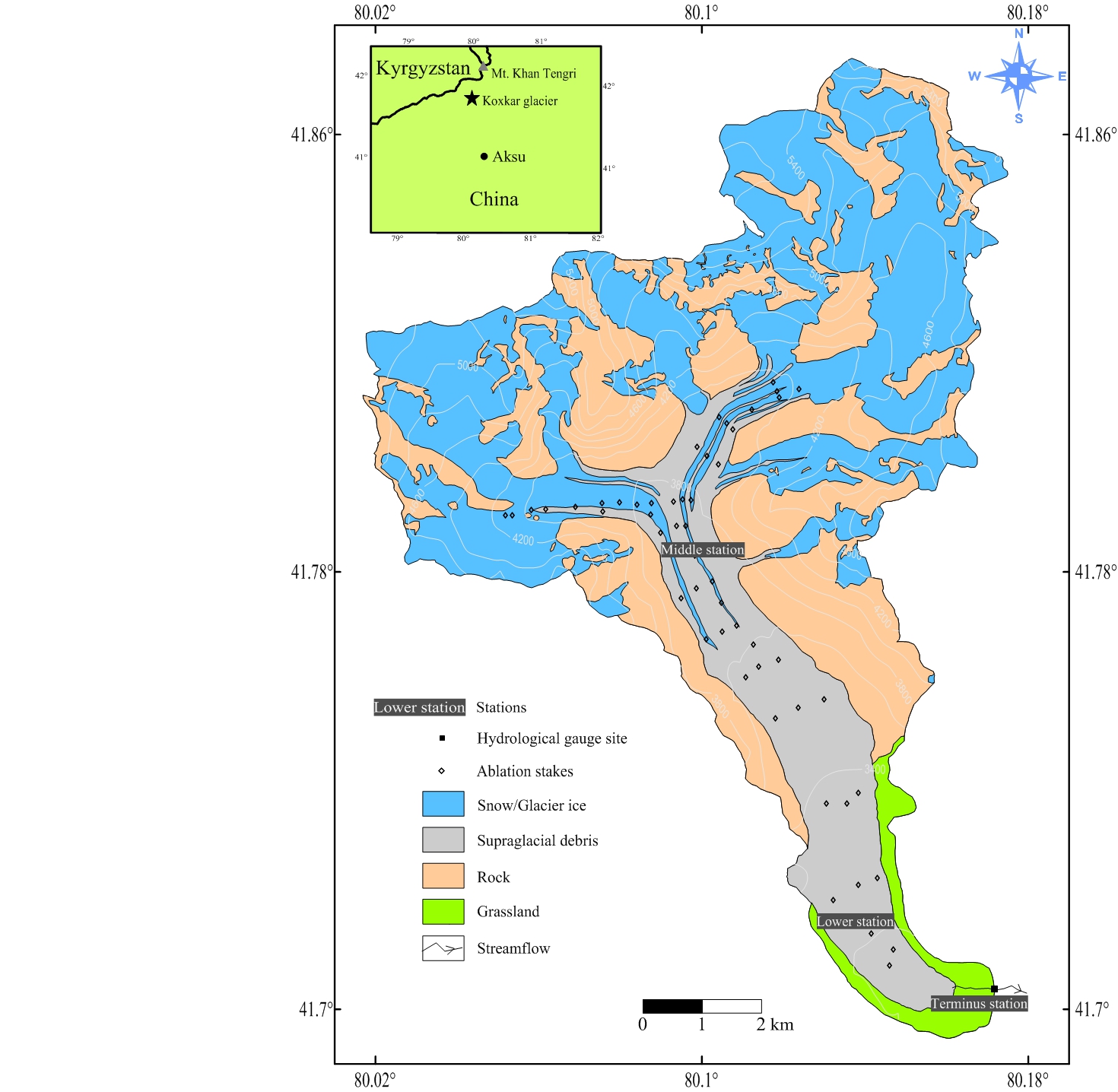




The Koxkar Glacier is a representative of such valley glacier under surveillance of the Koxkar site. It originats from Mt. Koxkar (6342 m a.s.l.) and flows southeast to the terminus of 3020 m a.s.l. The glacier extends 25.1 km in length and covers an area of 73.2 km2. The equilibrium line occurs at 4300 m a.s.l. in the icefall from whose foot a 15.5-km-long, debris-mantled glacier tongue appears. The supraglacial debris covers an area of about 20.8 km2, which accounts for 68.2% of the total ablation area. The thicknesses of debris layer range from less than 0.01 m on the upper reach of the ablation area and on ice-cliff faces to more than 3.0 m near the glacier snout (Figure 2). The Koxkar glacier catchment covers an area of 116.5 km2, out of which glacierized area, rock slope and grassland account for 62.8%, 33.9% and 3.3%, respectively.The mean annual air temperature observed near the terminus of the glacier is 0.30 ºC, whilst the mean summer temperature is 8.62 ºC. The melt season over the Koxkar glacier starts in late-April and continues for six months until late-October. Mean annual precipitation near the terminus is ~ 524 mm, of which > 80% occur during the melting period (Han et al. 2008). The mean runoff measured near the snout is ~102.86 × 106 m3 a-1, of which 93.6% occur during the ablation season.
Short term measurements on meteorology, glacial runoff and mass budget were carried out during June 2003 and August 2006, aiming at deriving relevant glacier natures to evaluate the meltwater runoff. Since April 2007, however, systemetic observations on glacier and meltwater variations were performed and three observational stations were established to provide continuous records of meteorological and hydrological data.